Intro
🤫 Tell you a secret, wallets are misleading. They do not store your crypto. In fact, they do not hold anything. So why do we need even them in dApps and Blockchain?
🧐 What are Wallets?
Wallets provide a way for Blockchains to identify you.
Like the traditional apps where we need to log in, you need to be authenticated in the Blockchain world every time you want to do something. But, in Blockchain, we don't use logins and passwords; we use a signature ✍️. And a wallet provides a way to stamp/sign.
Instead of having a dozen user accounts with Google, Twitter, etc.. you have one identity, that identity, that pen, that signature, that stamp sits with you and can be used everywhere.
You show the gatekeepers your pen, your signature; the chain acknowledges your identity, and boom, welcome to web3 land!
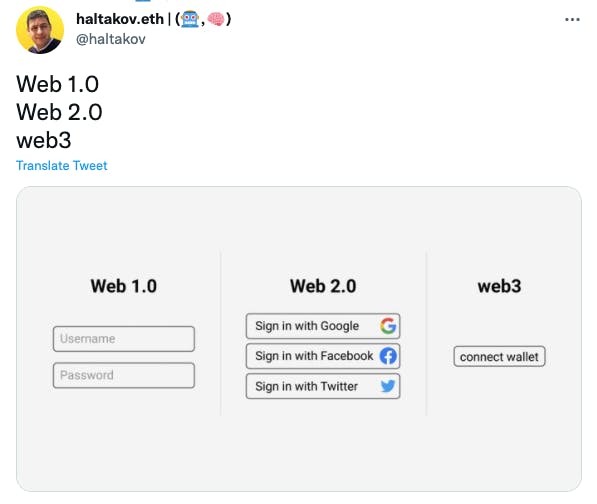 Source: @haltakov.eth
Source: @haltakov.eth
By the way, you can also create multiple wallets if you want various identities.
🤷♂️ Why do we need Wallets?
Now you are thinking.. we were just fine with user accounts. Who had the bizarre idea to create wallets, and why do you even care?
To understand why we need wallets, you first need to understand Blockchains. When I started, it was tough to picture what a Blockchain was; where is it? Is it on the Cloud? Who owns it? Does yet another Internet Company own that?
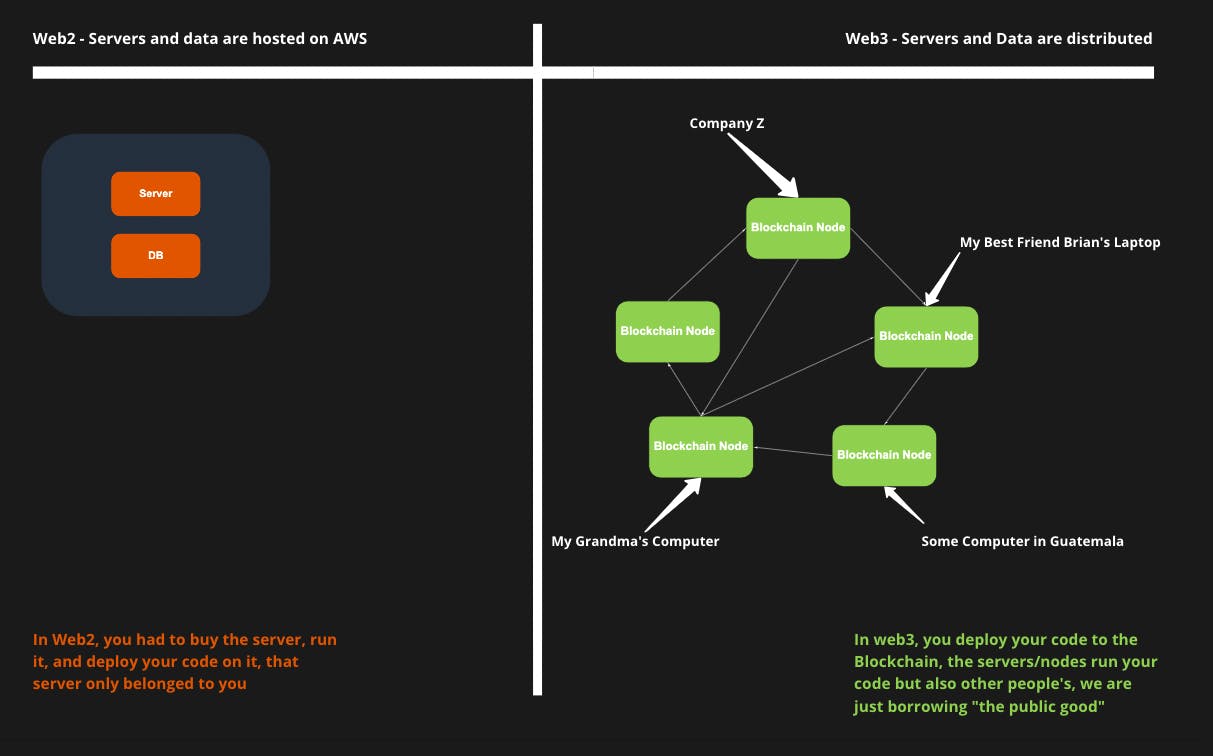
A blockchain is a distributed database:
- Blockchain is not one single thing. It is a swarm of servers, like 🐝
- Altogether, these servers represent "a Blockchain," like a beehive 👁🗨
- These servers belong to no one or rather anyone.
- Anyone can be part of the Blockchain, and you can use your grandma's laptop as one of these servers.
Put on your Web2 Glasses 👓
Given the few points we mentioned earlier, let's think about it from a traditional point of view. If anyone can be part of the Blockchain, what does it mean? It means data could be anywhere from your grandma's laptop to your worse enemy. In that case, how do I make sure that if I store data, the data only belongs to me:
- If an Instagram Clone were built on the Blockchain, you would not want anyone to start modifying or deleting your photos, would you?
- Or, if we were creating a Paypal or Stripe version on the Blockchain, how do we make sure that someone doesn't withdraw money from your account? After all, the data is duplicated and spread between everyone.
Let's illustrate this with the case of payments, pictures, or anything else is pretty much the same problem; it is just data in the end. So as we said, data are duplicated between servers/nodes. The balance sheet should be identical between every server.

😱 What prevents the Evil Guy's from changing the balance sheet and adding a "SEND transaction" 1 eth from Grandma? After all, he also gets a copy of the balance sheet to add anything he wants.
And now put on your Web3 Glasses 🕶
How do you protect something in your Dropbox or your Google Drive = by using a password to the link. Wallets provide a way to authorize things.

That's what wallets are here for. They provide a convenient way to password protect your data, but instead of a password, we use a signature, the wallet sign everything you do (transactions) in the Blockchain. The wallet signature ✍️ proves that you own that piece of data, that URL, that text, that token, and thus have the permission to do anything with it.
🌏 A World of Transactions
So grossly speaking, a Blockchain or a Blockchain Node, more precisely, is just a very long list of transactions, where every row is an action.
A Blockchain can do much more than Transfer Tokens, but the same logic applies to every action, especially for modifying data, where you need to prove that you have the permission to do so, and thus you need to sign that action (transaction).
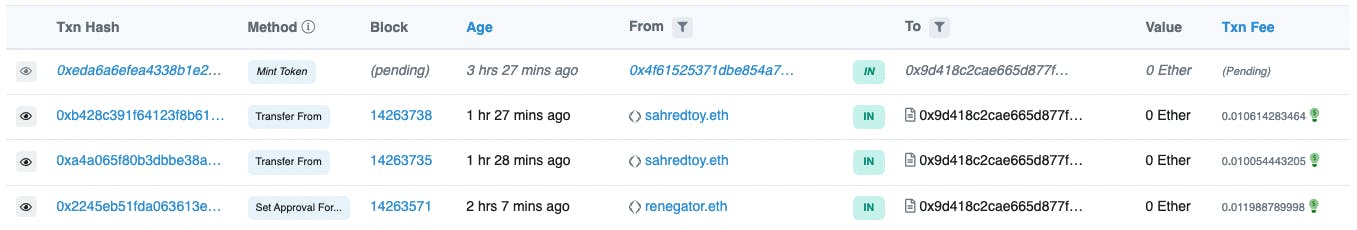
Transaction != Transfer, a transaction means a "change" or "action" here is an example of other types of actions. Please look at the Method column.
😉 Your Crypto is not inside your Wallet
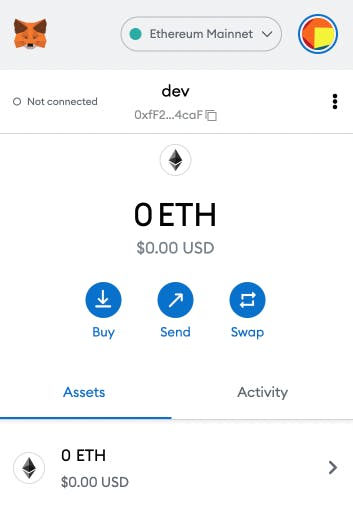
Finally, a note on crypto, this screenshot is the most misleading thing about wallets. Wallets do not store your crypto. In fact, they do not hold anything, they are just a UX layer above your private key.
Try it for yourself
ttps://etherscan.io/address/0x9d418c2cae665... How come you can read someone else balance if the crypto were living in the Wallet? This would be the same thing for a USB Ledger. If you got the public address, you can look up the balance yourself and see everything they did.
A Wallet is a safe way to stamp and sign transactions. So Wallet Apps such as Metamask conveniently show you your balance as recorded in the Blockchain. And use the molded signature ✍️ to sign transactions, send money, connect to dApps, etc.
🌀 Putting things back in order
- To the core, private keys (the stamp or signature) are necessary to sign transactions. Regardless of if the action is a token transfer or something more advanced. That is how we can ensure authentication and permissions in the Blockchain world.
- Thanks to cryptography, we can derive public keys from a private key. The public key or the public key hash is what we call the public address or the wallet public address.
- Wallets are just a convenient concept we created around private and public key pairs. When we talk about identifying a wallet, we identify it by "public address." A wallet can sign a transaction using cryptography and the private key.
- Wallet Apps are just products such as Metamask, Phantom, Argent that put features on top of all of these.
So here you have it, public/private key pairs provide a way for the Blockchain to identify you and make sure you got the permission to do what you claim you should be able to do.
I hope this clarifies your understanding of Blockchain and why we need Wallets!
Please subscribe for more web3 tutorials or drop a comment 👇👇🏾👇🏻 if you find this helpful or want to say hi!
Going Further
Learning about Ethereum Smart Contract Methods

